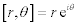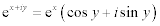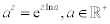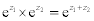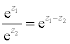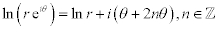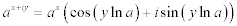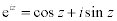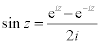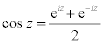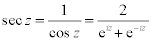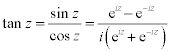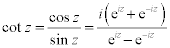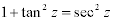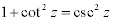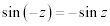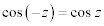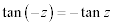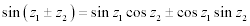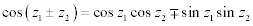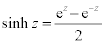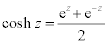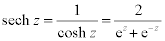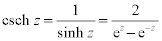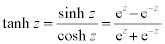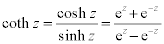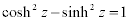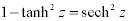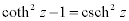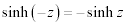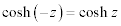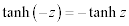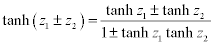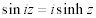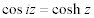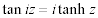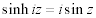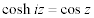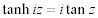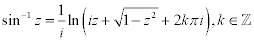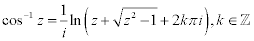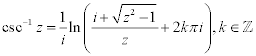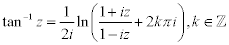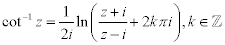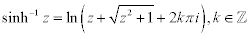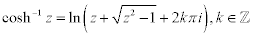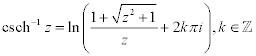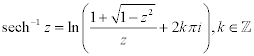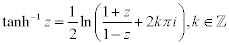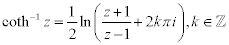| Complex Numbers |
| MORE ON COMPLEX NUMBERS |
| Note: Some textbooks use the letter j to represent the imaginary part of a complex number. I have used the more universal i throughout. |
| A complex number, z, is of the form: |
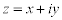 |
| or, using polar coordinates: |
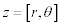 |
| where x and y are real numbers and: |
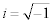 |
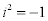 |
| The modulus of a complex number is: |
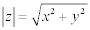 |
| The argument of a complex number is: |
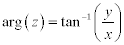 |
| The conjugate of a complex number is: |
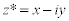 |
| In the following lines: |
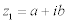 |
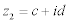 |
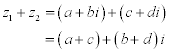 |
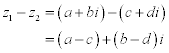 |
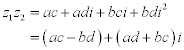 |
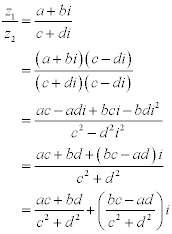 |
| For z = x + iy and where y is measured in radians: |
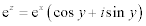 |
When 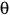 is measured in radians: is measured in radians: |
| The exponential form of a complex number: |
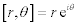 |
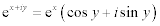 |
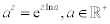 |
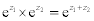 |
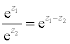 |
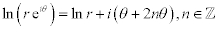 |
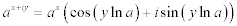 |
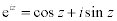 |
| Complex Trigonometric Functions: |
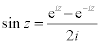 |
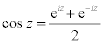 |
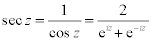 |
 |
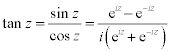 |
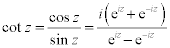 |
| Complex Trigonometric Function Properties: |
 |
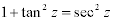 |
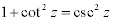 |
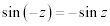 |
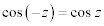 |
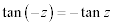 |
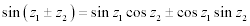 |
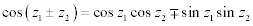 |
 |
| Complex Hyperbolic Functions: |
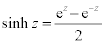 |
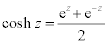 |
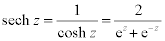 |
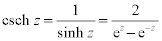 |
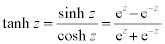 |
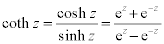 |
| Complex Hyperbolic Properties: |
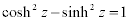 |
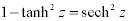 |
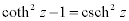 |
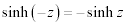 |
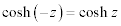 |
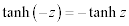 |
 |
 |
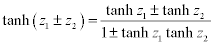 |
| Complex Trigonometric and Hyperbolic Function Relations: |
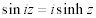 |
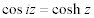 |
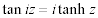 |
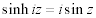 |
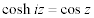 |
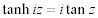 |
| Complex Inverse Trigonometric Functions: |
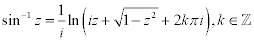 |
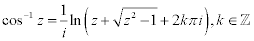 |
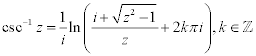 |
 |
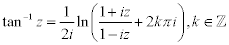 |
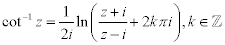 |
| Complex Inverse Hyperbolic Functions: |
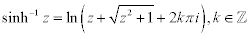 |
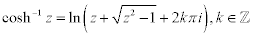 |
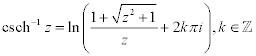 |
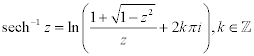 |
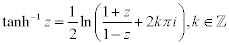 |
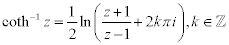 |

 Printer Version
Printer Version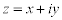
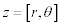
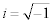
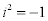
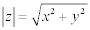
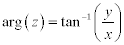
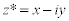
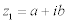
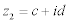
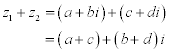
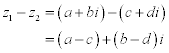
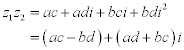
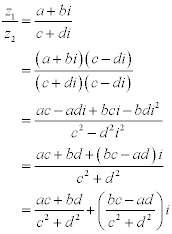
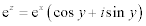
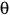 is measured in radians:
is measured in radians: