| SI Derived Units With Special Names |
| Quantity | Name | Symbol | Expression in terms of other units | Expression in terms of SI base units |
| Frequency | hertz | Hz | | s-1 |
| Force | newton | N | | m kg s-2 |
| Pressure / Stress | pascal | Pa | N/m2 | m-1 kg s-2 |
| Energy / Work / Quantity of Heat | joule | J | N m | m2 kg s-2 |
| Power / Radiant Flux | watt | W | J/s | m2 kg s-3 |
| Electric Charge / Quantity of Electricity | coulomb | C | | s A |
| Electric Potential / Potential Difference / Electromotive Force | volt | V | W/A | m2 kg s-3 A-1 |
| Capacitance | farad | F | C/V | m-2 kg-1 s4 A2 |
| Electric Resistance | ohm | 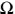 | V/A | m2 kg s-2 A-1 |
| Electric Conductance | siemens | S | A/V | m-2 kg-1 s3 A2 |
| Magnetic Flux | weber | Wb | V s | m2 kg s-2 A-1 |
| Magnetic Flux Density | tesla | T | Wb/m2 | kg s-2 A-1 |
| Inductance | henry | H | Wb/A | M2 kg s-2 A-2 |
| Celsius Temperature | degree celsius | °C | | K |
| Luminous Flux | lumen | lm | | cd sr |
| Illuminance | lux | lx | lm/m2 | m-2 cd sr |
| Activity of a Radionuclide | bequerel | Bq | | s-1 |
| Absorbed Dose / Specific Energy Imparted / Kerma / Absorbed Dose Index | gray | Gy | J/kg | m2 s-2 |
| Dose Equivalent / Dose Equivalent Index | sievert | Sv | J/kg | m2 s-2 |

 Printer Version
Printer Version
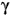 rays)
rays)